
OFFICIAL PRESS RELEASE
Stuttgart, Germany, Nov 05, 2007
Origins in coach-building
* Coach body design taken over by the automobile
* Landaulet body once highly popular for taxicabs
The body form of the landaulet, or �half-landau� as it is sometimes known, owes much to the construction of horse-drawn coaches. The landau (or sometimes �Landauer� in German) was an open coach, probably named after the town of Landau in the Palatinate region of Germany. The passengers sat facing each other, and could be protected by two half-roof sections, pulled over them from either end of the vehicle when required. The coachman sat on a box seat, well away from the passenger compartment. The landaulet structure differed in that it only had the rear half-roof covering. And depending on the design, the driver�s compartment in front of the passenger seats could have a rigid roof, a glass top or a front windshield.
At the end of the 19th century the customary distinction in coach construction between the landau and landaulet was carried over into automotive design, with Daimler and Benz both initially making cars with landaulet and landau bodies.
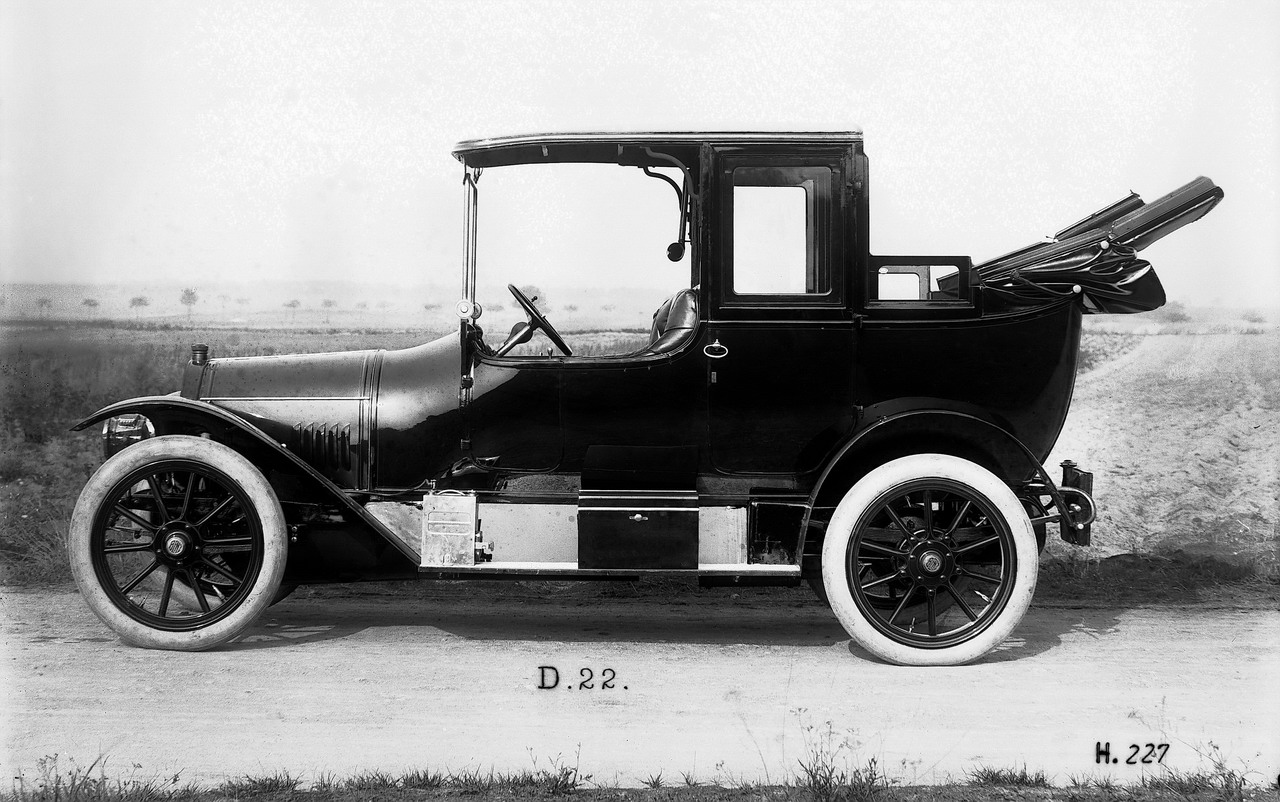
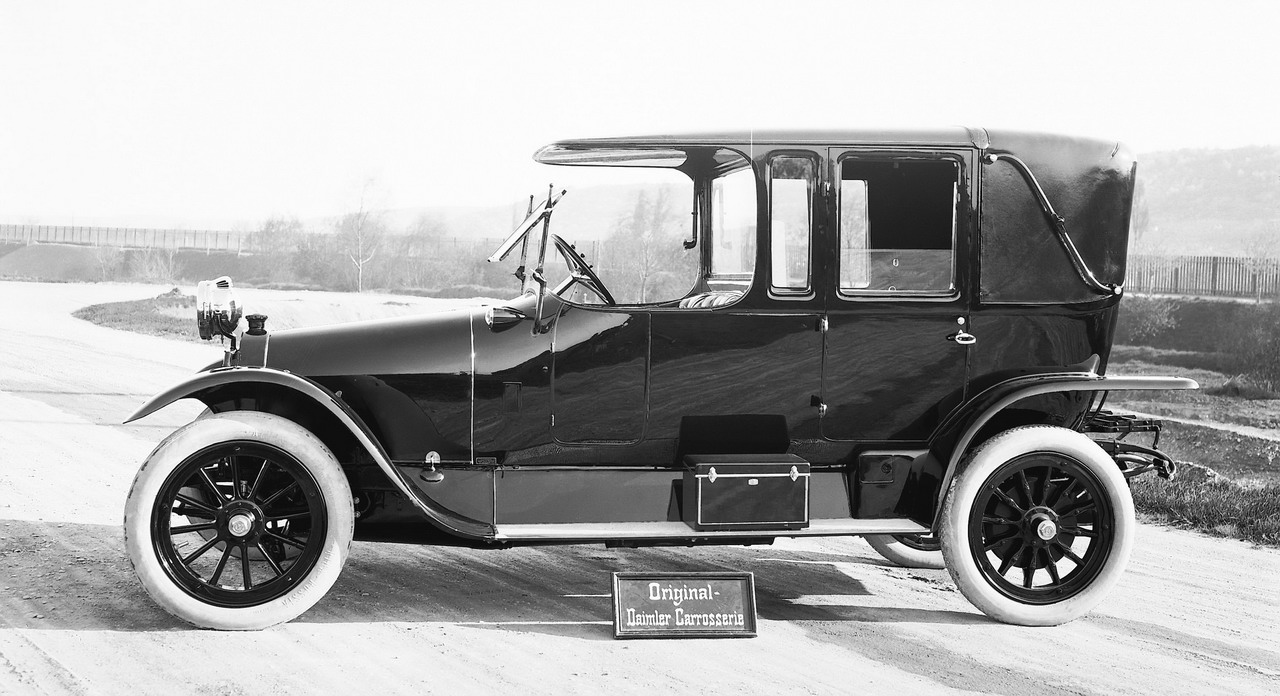
Glory days of the landaulet
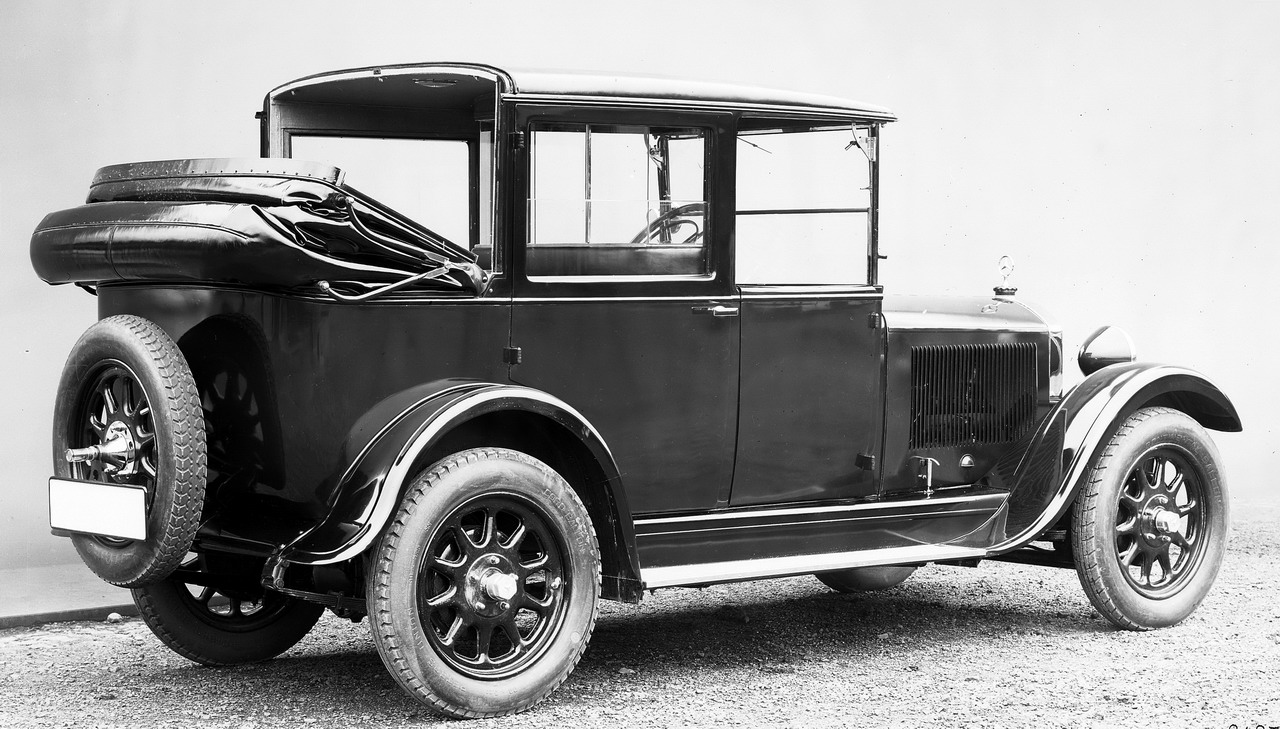
But events were to prove that only the landaulet had a viable future in the age of the automobile. One of the reasons was clearly that as speeds increased, passengers became more reluctant to sit with their backs to the direction of travel. The landaulet design emerged as the accepted form, and became increasingly popular with customers. But during the heyday of landaulet bodywork in the first half of the 20th century there was still no consistent or standard design.
One of the major points of difference was in the area of the driver�s seat. The box-seat of the Daimler belt-driven landaulet of 1896 for use as a taxi left the driver completely unprotected. In comparison, a 25/45 hp Benz landaulet from 1910 offered the driver a windshield and a rigid roof, but no doors or side windows. Side doors � but still no windows � were added in the 8/20 hp Benz of 1912.
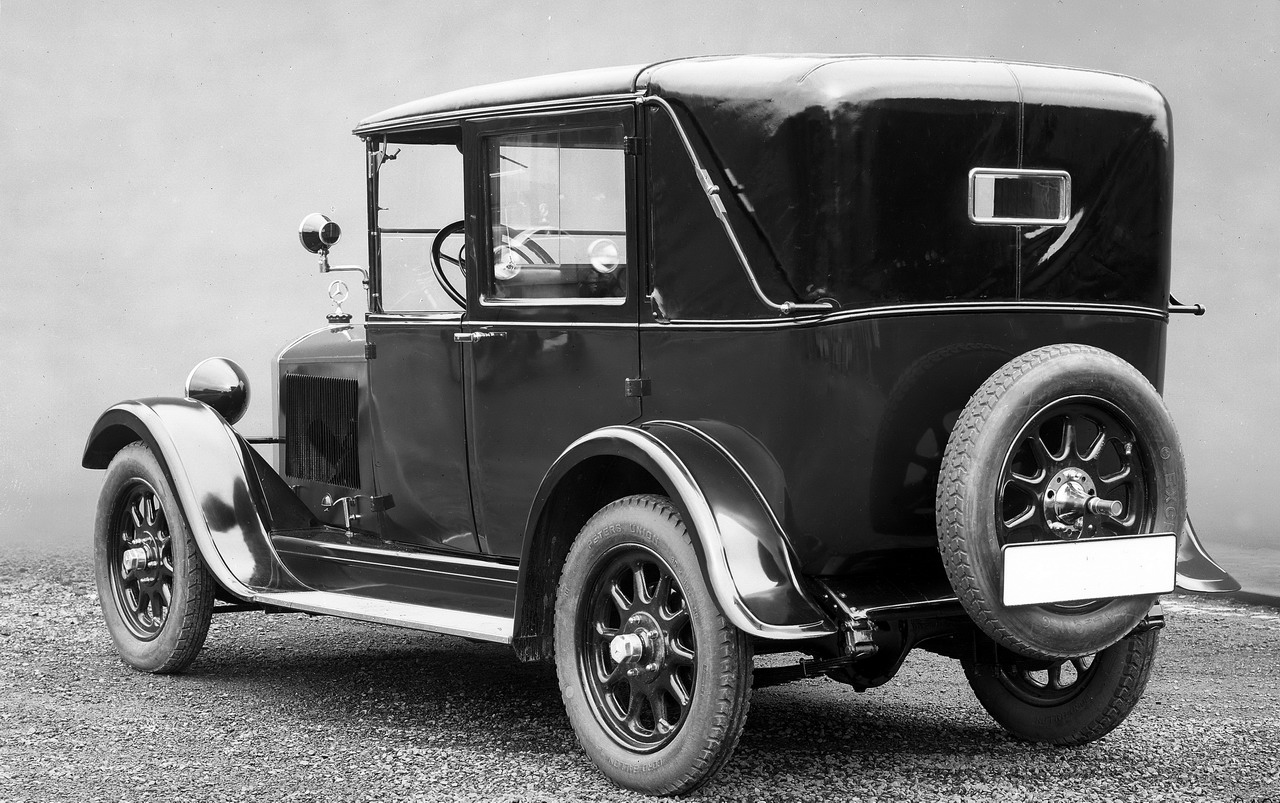
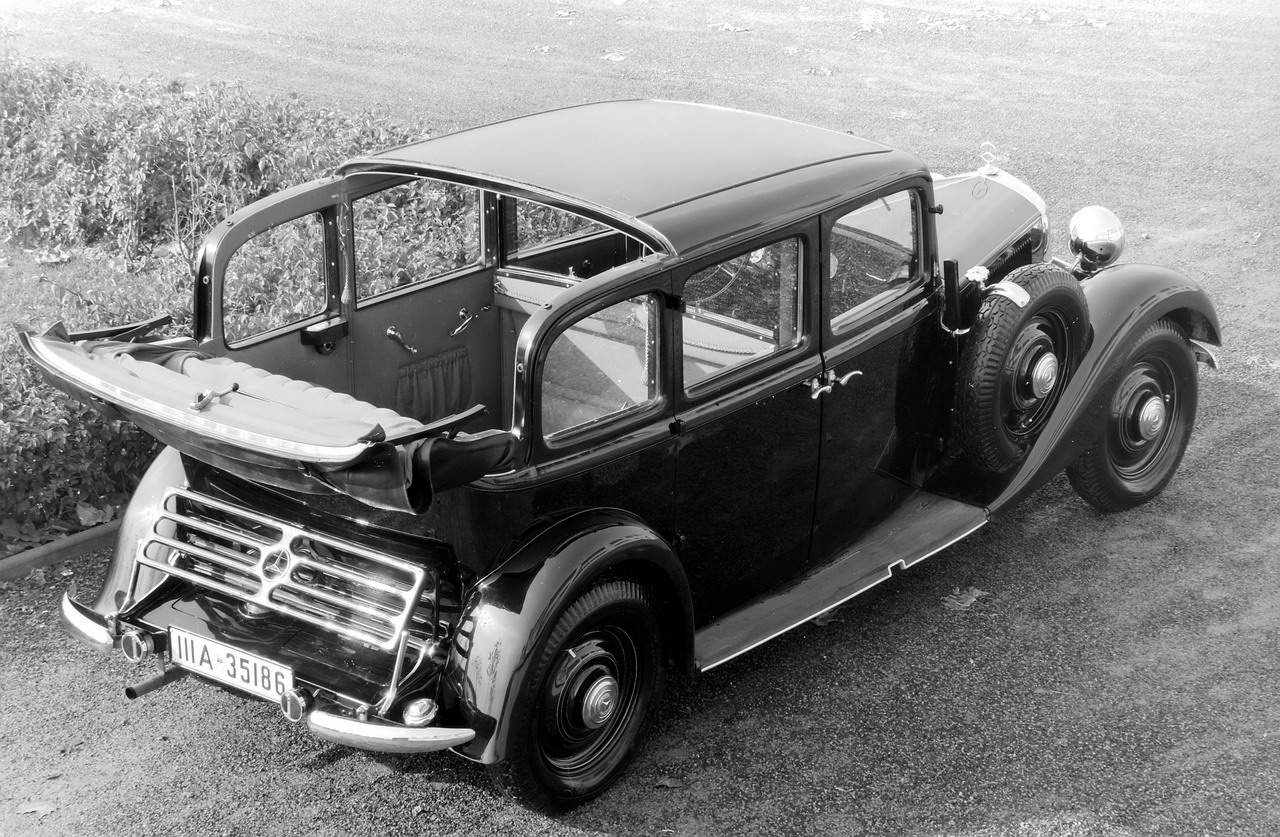
Subsequent landaulet models reversed the principle of leaving the chauffeur out in the open - the driver was now protected by a windshield on all sides, as in a limousine, but the folding convertible top over the rear seats continued to offer flexibility for the passengers. This more contemporary form of the landaulet was used in luxury models such as the 15/70/100 hp Mercedes-Benz 400 Pullman landaulet from the late 1920s, and also in the landaulet taxicabs based on the Mercedes-Benz 260 D from 1936.
Landaulet as a taxicab
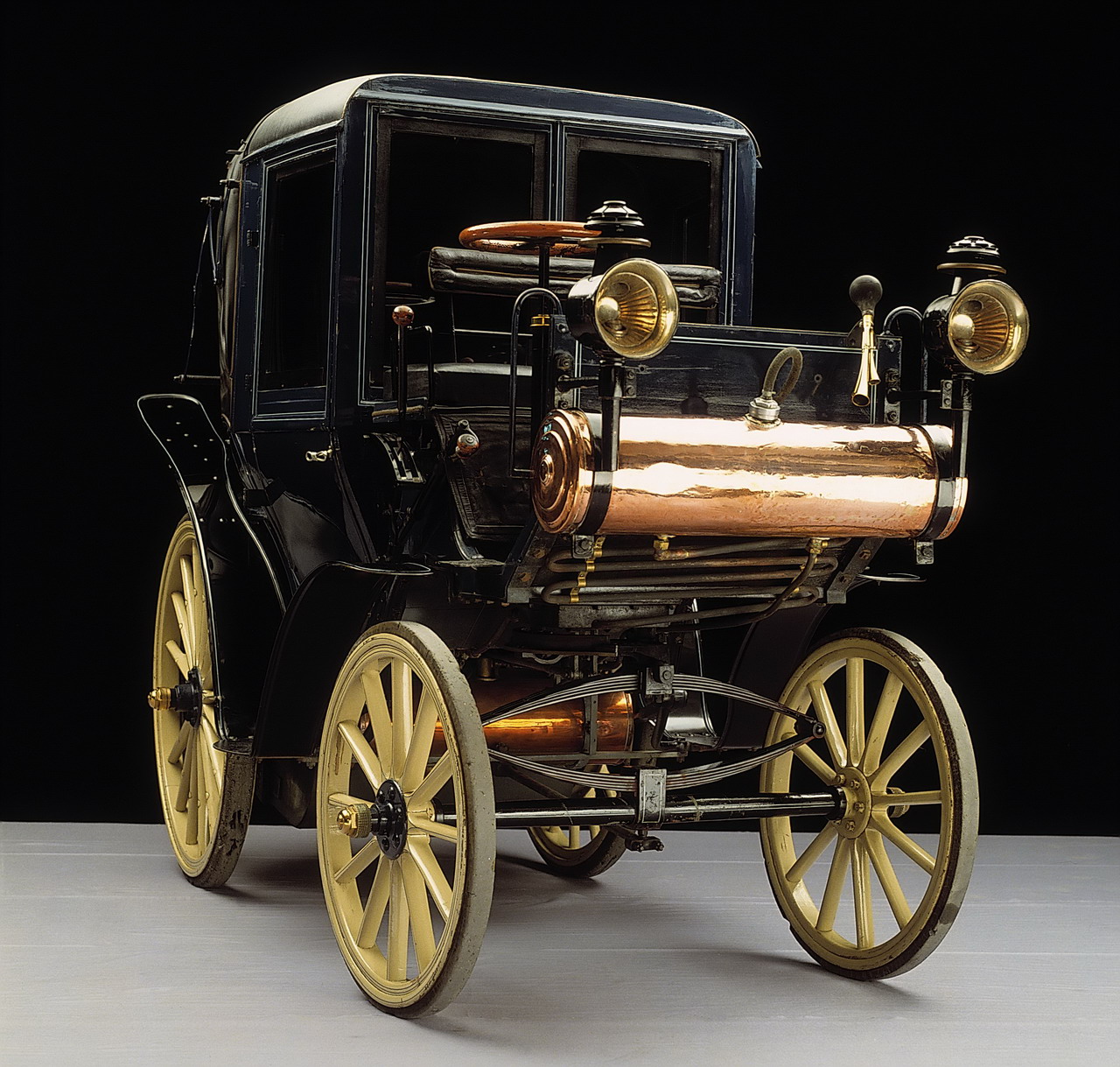
Al fresco motoring proved particularly attractive to taxicab customers � as indicated by the large numbers of taxicabs supplied with a landaulet body. In fact a landaulet became the world�s very first taxi when a Stuttgart-based haulage and taxicab operator, Friedrich August Greiner, ordered a Victoria landaulet with a taximeter from Daimler-Motoren-Gesellschaft (DMG) under order no. 1329. The vehicle was duly delivered in May 1897, and the world�s first motorized taxi went into service in June, once the required permit had been obtained from the police. The vehicle cost its owner the small fortune of 5530 Mark. Included in that price were the landaulet half-convertible top, two dash leather coverings, reverse gear and solid rubber tires.
In the following decades both Daimler and Benz, and from 1926 Mercedes-Benz, supplied taxis based on this distinctive body design. The 12/30 hp Benz was actually marketed from 1913 to 1914 solely as a taxicab landaulet. In this period the landaulet became just as popular with taxi passengers as with VIPs. However the design was never in high demand for private automobiles for everyday use. In his reference work entitled �The modern automobile and its maintenance and repair� and published in 1921, Max Peter wrote: �The advantages of open-top and closed-top vehicles are to some extent combined in the landaulet which can be driven as either. Because of the ability to adapt the body structure according to the season, this body design is associated above all with taxi automobiles, and probably for this reason it is less popular for private cars, notwithstanding its undeniable advantages.� This quote is taken from the section dealing mainly with taxis and private cars of the traditional kind. The �elegant landaulet�, in contrast, is classified under a separate category specifically for parade cars.
Evolution of an elite body design
The folding convertible top design as a luxury variation on the automobile was discussed by authors Ernst Misol and Hermann Klaiber in 1913 in their book entitled �What do I need to know about my car, and how should I drive it to comply with the authorities� regulations?� Misol and Klaiber emphasized the advantages of different body styles for different purposes: �A luxury car used only in city traffic should always have a fully enclosed body, i.e. the limousine design. But for shorter journeys outside city limits, preference is to be given to the landaulet with its retractable top at the rear.�
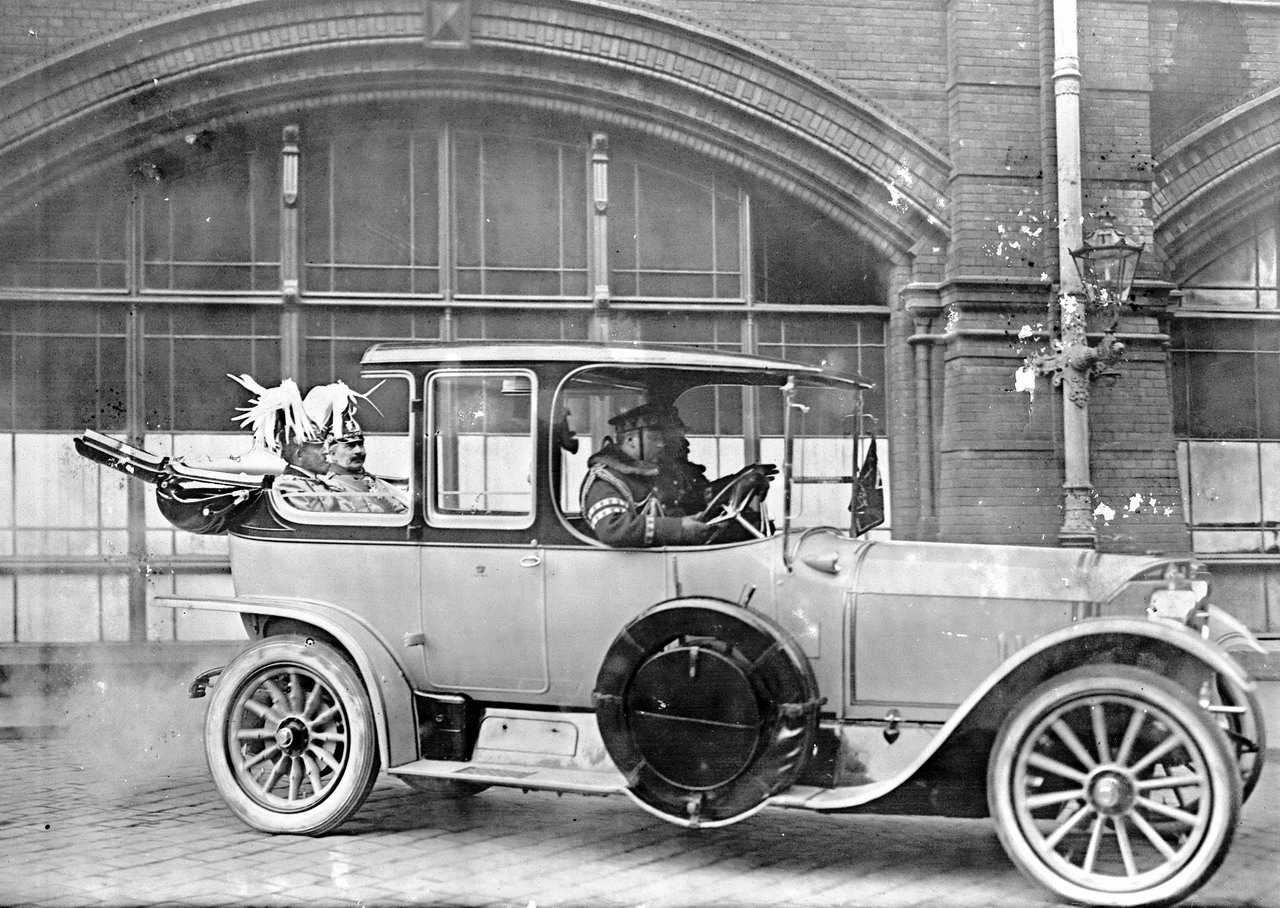
Owners of luxury landaulet cars in the pre-World War I period included Emperor Wilhelm II. The emperor�s first vehicle of this type was a 39/75 hp Mercedes chain-driven landaulet, which he used as a traveling car. This was followed in 1911 by a 38/70 hp Mercedes landaulet for the same purpose. The emperor then chose a 28/60 hp Mercedes landaulet as a city car in 1913. And during a visit by the heir to the Romanian throne in 1913, the monarch and his guest were driven through the streets in a 26/65 hp Mercedes-Knight landaulet.
Following the end of the imperial era, in 1938 Mercedes-Benz presented Paul von Hindenburg with a 12/55 hp Mercedes-Benz 300 six-seater landaulet: Hindenburg had been elected as President of the Weimar Republic in 1925, as the successor to Friedrich Ebert.









Copyright � 2008, car-evolutioncars. All rights reserved.

















No comments:
Post a Comment